Notes
Introduction
This article explains how to install Ollama and LM Studio and run a mastra sample.
Poem
Since the appearance of GPT-2, LLMs (Large Language Models) have dominated the conversation. It feels like every month OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, Alibaba announce something LLM-related.
Thanks to that, general users can use tools like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Qwen.
Each tool has its strengths, but the front-runner in this field is likely OpenAI. Anyone following (US) stock markets can feel the "AI bubble" heat; whether it is justified depends on whether LLM companies like OpenAI can monetize. Of course, not only the "pickaxe sellers" but also the companies using the pickaxes must make profits for sustainability.1
Services like Artifact appeared but already ended. Companies are adding AI features to existing services, but for consumer services, it seems hard to justify charging users for "new value". Of course, improving UU (Unique User) or CVR (Conversion Ratio) could raise revenue and profits. But right now, it feels like only the companies that build LLMs and ship them as services can directly monetize them. In the end, the question is how to replace human work with LLMs to reduce costs and raise margins, and whether the time saved can be used to find sustainable monetization for LLM-powered services. It seems companies are pushing LLM integration for fear of missing the trend or under shareholder pressure, even at the expense of profit.
That said, I think cost concerns may fade in the near future. For many use cases, current performance is already sufficient. So competition will likely move toward price and compute efficiency. Large models will keep developing, but the need to chase them will diminish, and business success will depend on delivering current-level accuracy and speed at lower cost.
I also think architectures combining SLMs (Small Language Models) will become mainstream, as some claim. Let an LLM decompose tasks into parts that an SLM can handle, let SLMs execute them, and let the LLM orchestrate the next steps. This already happens in GPT-5 and Claude Code, and likely in agent workflows.2 As SLMs improve in capability and specialization, the cost per token should fall further.
Finally, LLM tech itself has room to improve. Transformer dominates now, but something better could emerge, or efficiency improvements may come without changing the architecture.
The US stock market will tell us the answer within a few years.
Intended audience
- People who want to develop with LLMs
- People who don't want to use Python
- People who want to build local AI agents
- People who want to develop with LLMs for free
- People comfortable with TypeScript
Local LLM
LLMs are trendy and many engineers want to try them. But for regular engineers like me, paying for APIs with unclear costs to "get a feel" is intimidating. If you can't monetize it, using LLMs just costs money, so even for hobby projects it's hard to commit.
There are a few options. One is to use a service like OpenRouter within free credits or free models. Another is to run LLMs locally.
Given speed and load, OpenRouter is probably better, but here we'll use local LLMs. I'll write about OpenRouter in a later article.
There are a few ways to run local LLMs. One is Ollama, another is LM Studio.
I'll explain how to install both. You can choose either, but later you'll see that mastra doesn't work with Ollama's official steps, so I recommend LM Studio. Also, LM Studio gives you a GUI chat UI, which is more approachable.
You might say "What about Open Web UI?" — it didn't work in my environment, so I excluded it.
Environment
Here is my environment before installation. I don't develop on Windows, so the steps are for macOS, but if you are trying LLM development, following the official install steps should be easy enough.
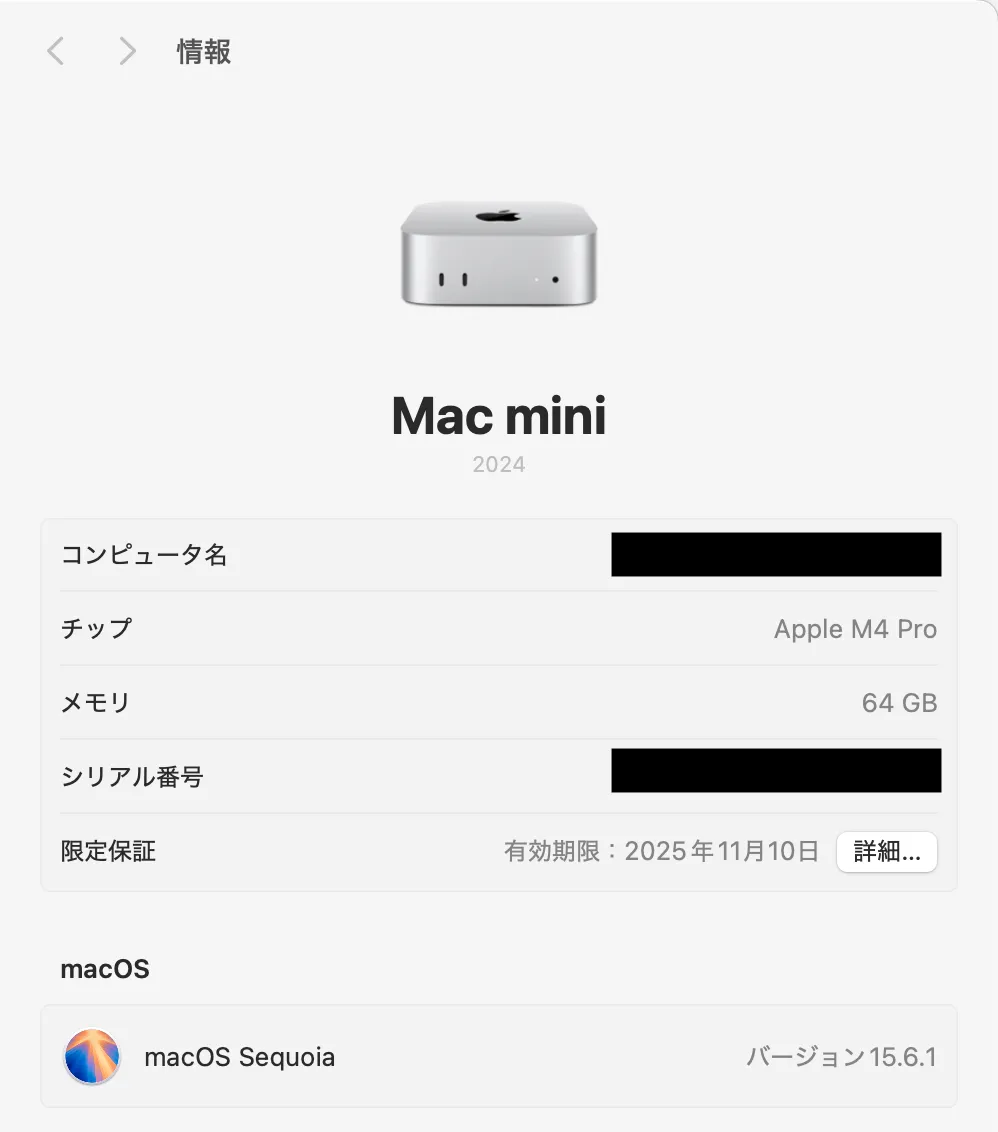
Running local LLMs requires decent hardware. Typical laptops or mid-spec desktops may be insufficient. It depends on the model, but I assume we can run gpt-oss:20b because I want tool usage. "Tool use" is explained later.
- Ollama
- LM Studio
- 0.3.30
- mastra
Ollama
Overview
Ollama is a tool to easily run LLMs locally. You can search models on the web, then run them by copying the command in the model page's top-right and executing it in the terminal.
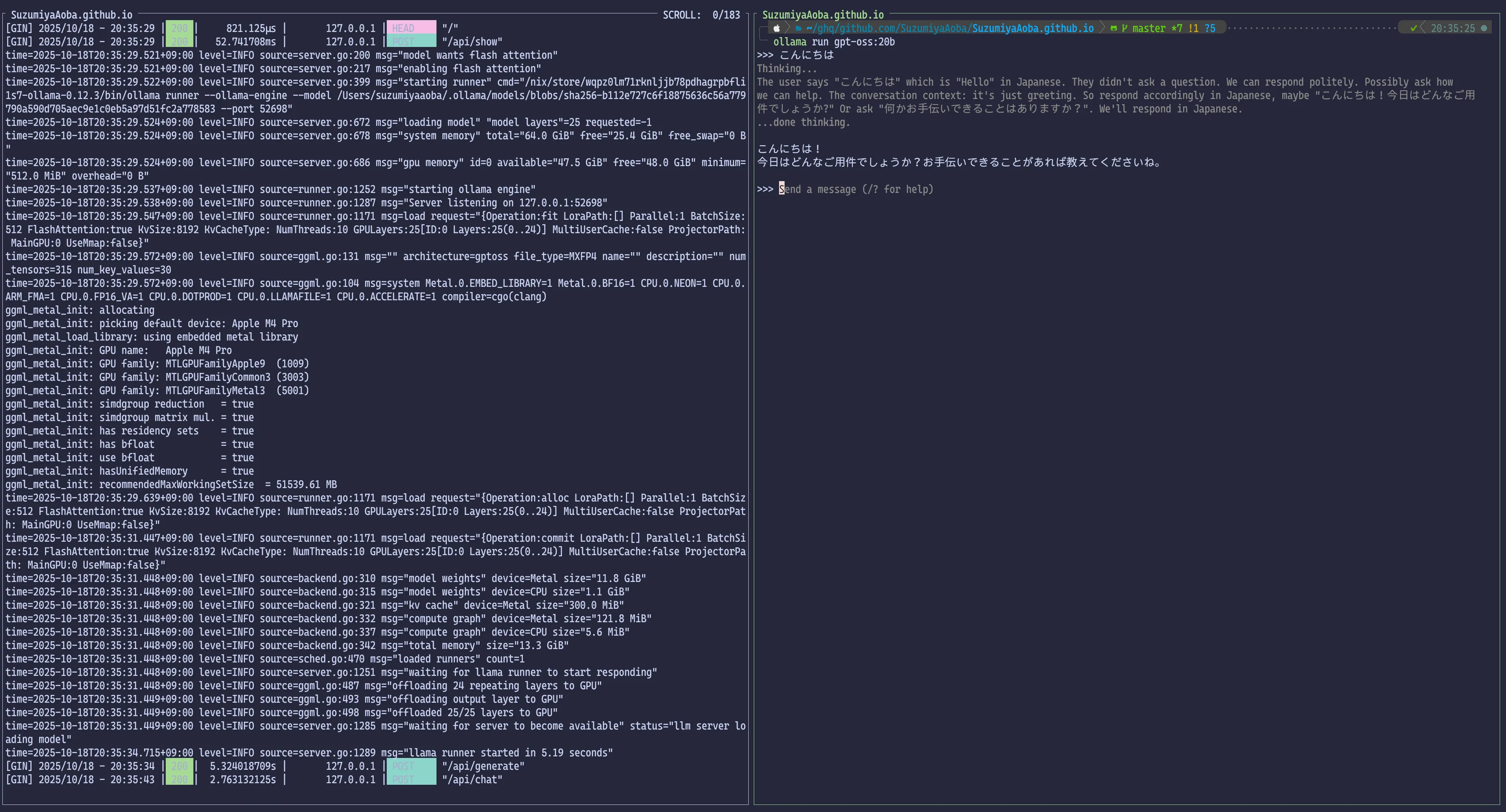
The UI is CLI-only, with no conversation memory, so it can feel less approachable.
Installation
If you use Homebrew, install with:
1$ brew install ollama
If not, use the method that suits your environment. I use nix-darwin + Home Manager, so I use Nix configs.
If you don't use a package manager, download the binary from the official Ollama site and follow the install steps.
Running
To use Ollama, first start the server:
1$ ollama serve
Then run a model; it will download the model and start a chat:
1$ ollama run gpt-oss:20b
Hardware warning
If your PC lacks enough specs for LLMs, it may freeze.
Make sure your machine can run gpt-oss:20b.
You likely need a decent GPU and at least 32GB (or 48GB) of RAM.
LM Studio
Overview
LM Studio is similar to Ollama but provides a GUI app. If you switch to Developer mode, it offers an OpenAPI-compatible API, which works well with mastra.
Installation
If you use Homebrew:
1$ brew install lm-studio
Otherwise, install using your environment's method. If you don't use a package manager, download the binary from the official LM Studio site and follow the steps.
Using LM Studio
Because we want to use it as an LLM API, switch to Developer mode after launching. When LM Studio starts, you see a GUI like this:
Click the magnifying-glass icon at the bottom-left to search and download models.
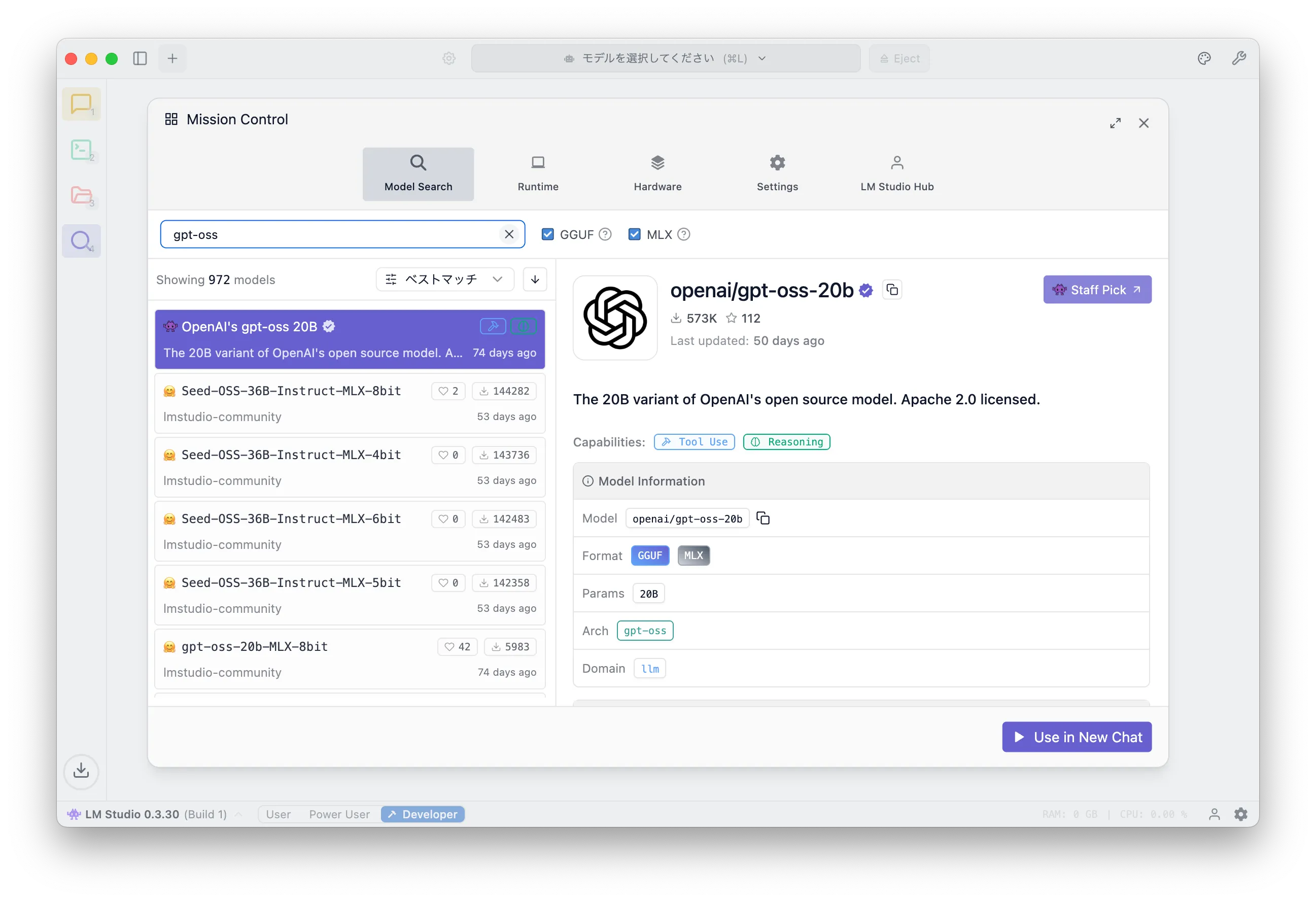
Search for gpt-oss and you'll see OpenAI's gpt-oss 20B. Click "Download" in the bottom-right.
The screenshot shows "Use in New Chat" because it's already downloaded.
After the download, click the second icon from the top (terminal icon). You should see a screen like this, where you can start a local server for the model.
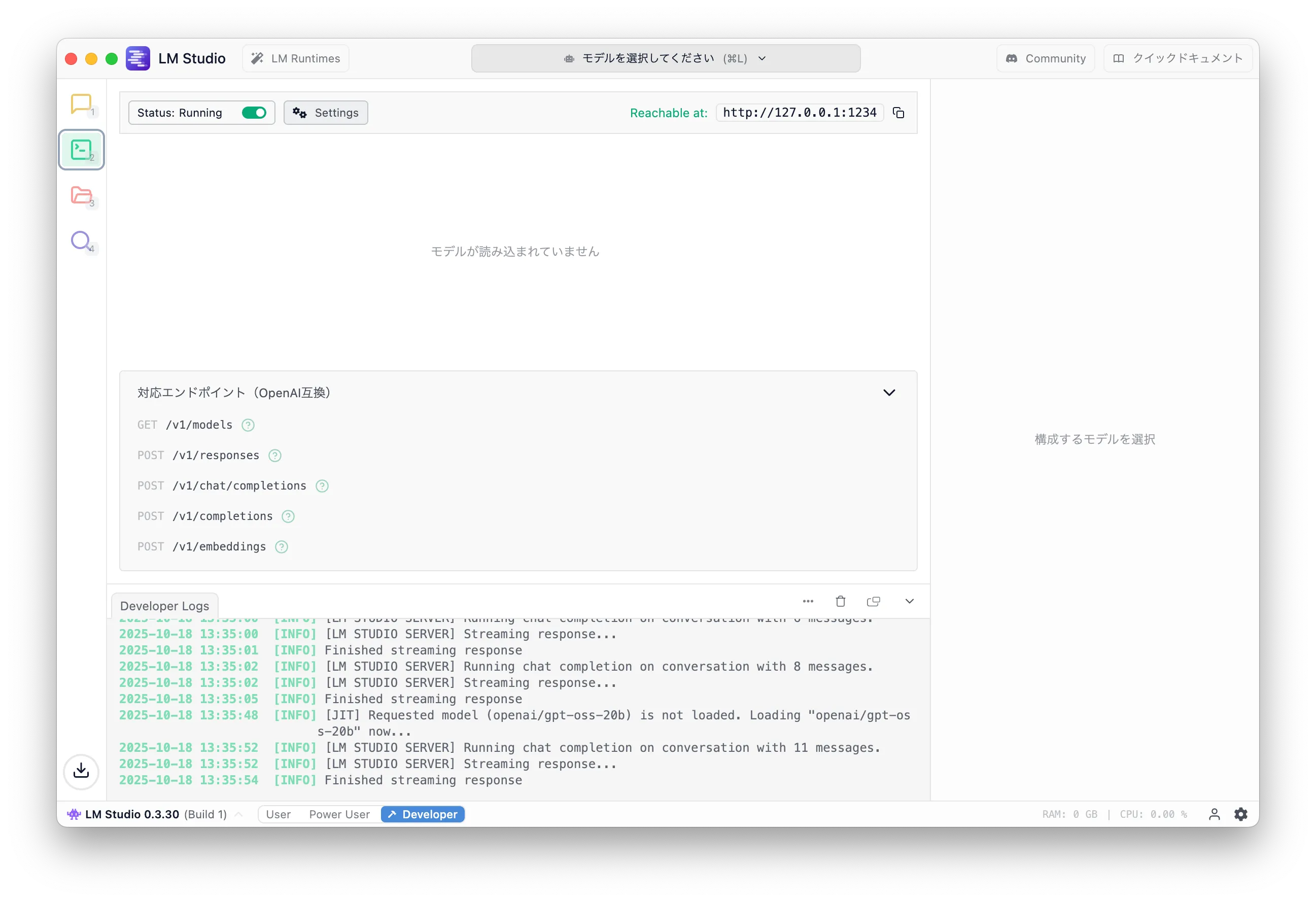
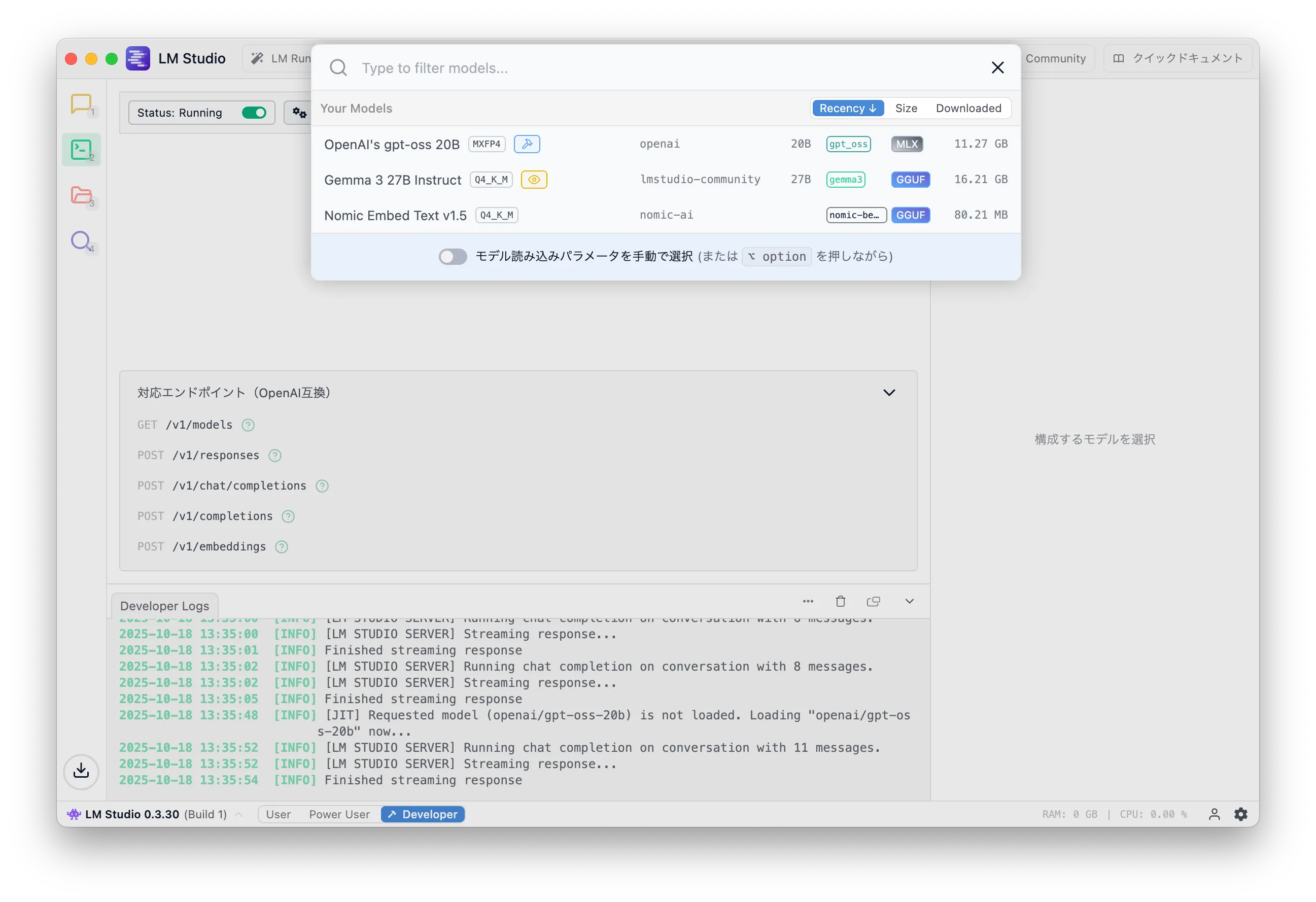
Click "Select a model" and choose "OpenAI's gpt-oss 20B".
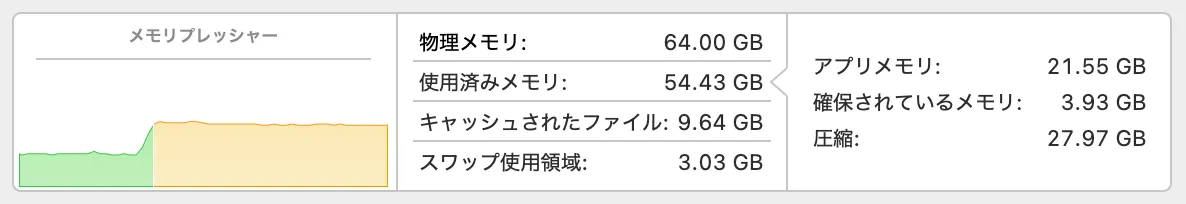
Loading a model consumes memory even before inference, as shown below.
After loading, click the top-left icon to open the chat UI and try a prompt.
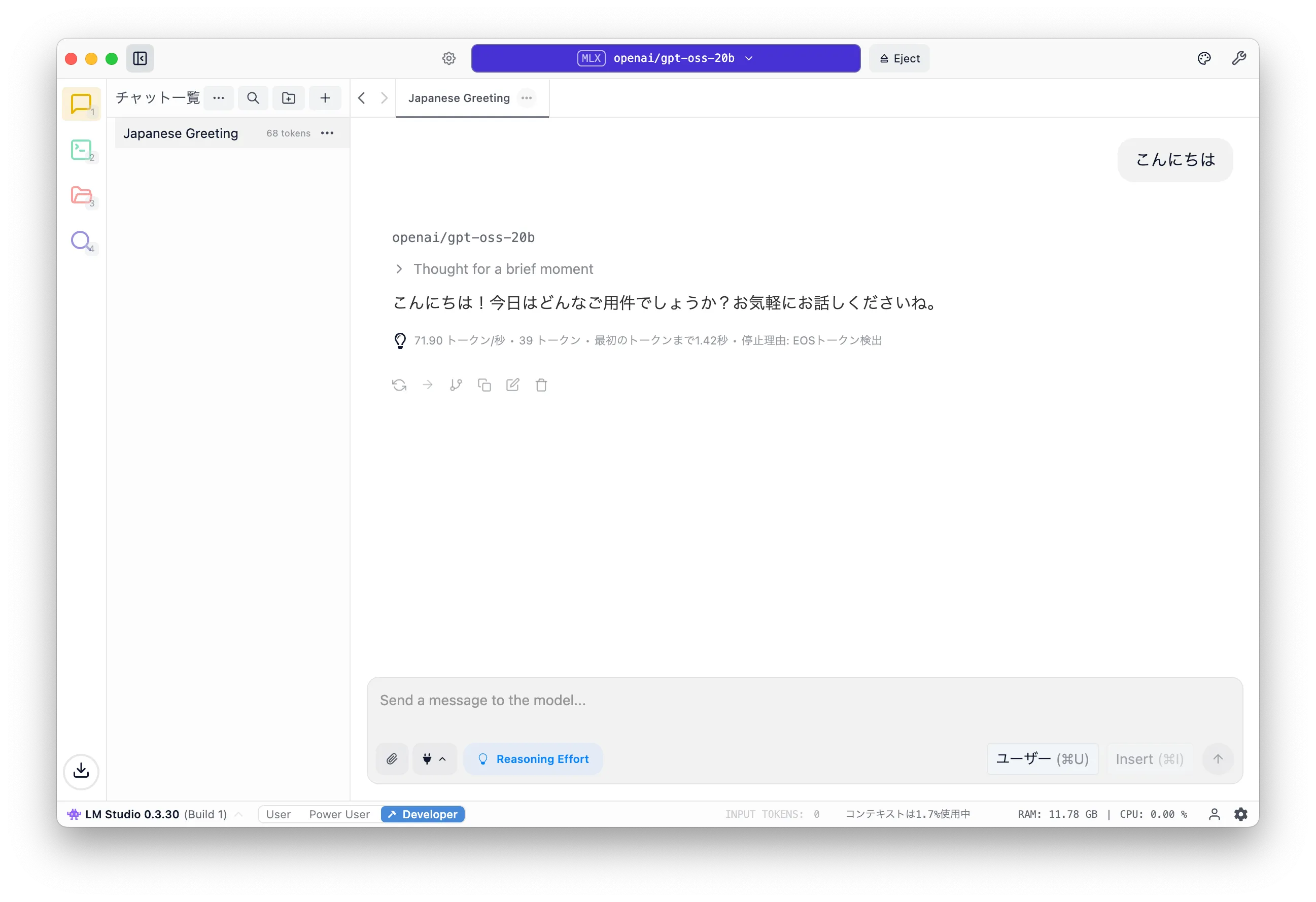
If you get a response, the LLM is working.
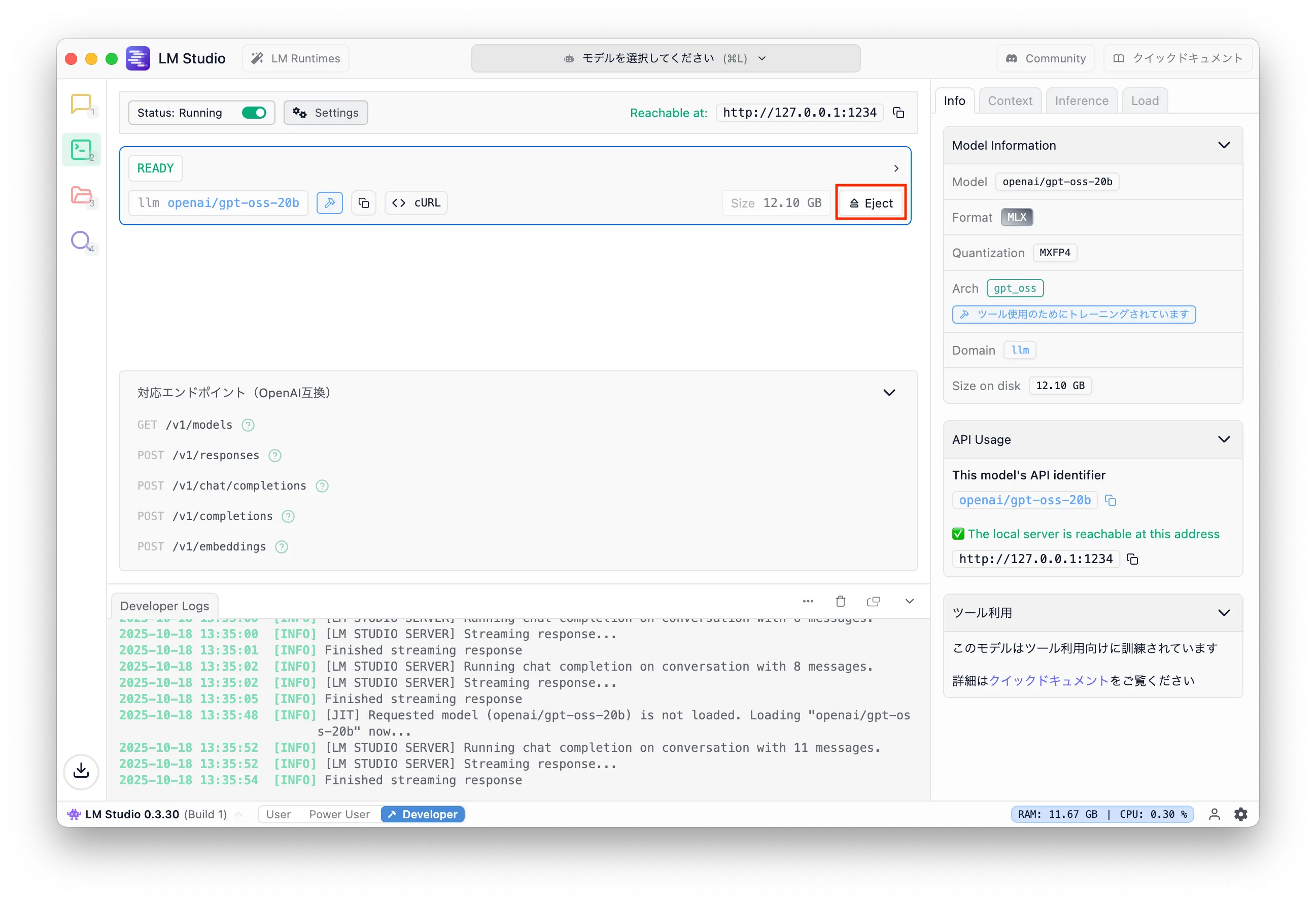
Finally, if you're done, eject the model to free memory. Click the Development icon and press "Eject".
mastra
Now the main topic: mastra.
Overview
mastra is a framework to build LLM-based AI agents in TypeScript. It's roughly like LangChain/LangGraph in Python (I might be wrong as I don't know them deeply).
For web engineers who don't want to learn Python, it's a perfect fit.
This time we will set up mastra and run the sample app using the API server started by LM Studio. If you use Ollama, even the tutorial doesn't work. It might work with OpenAPI-compatible mode, but I might run out of energy before that.
Create a project
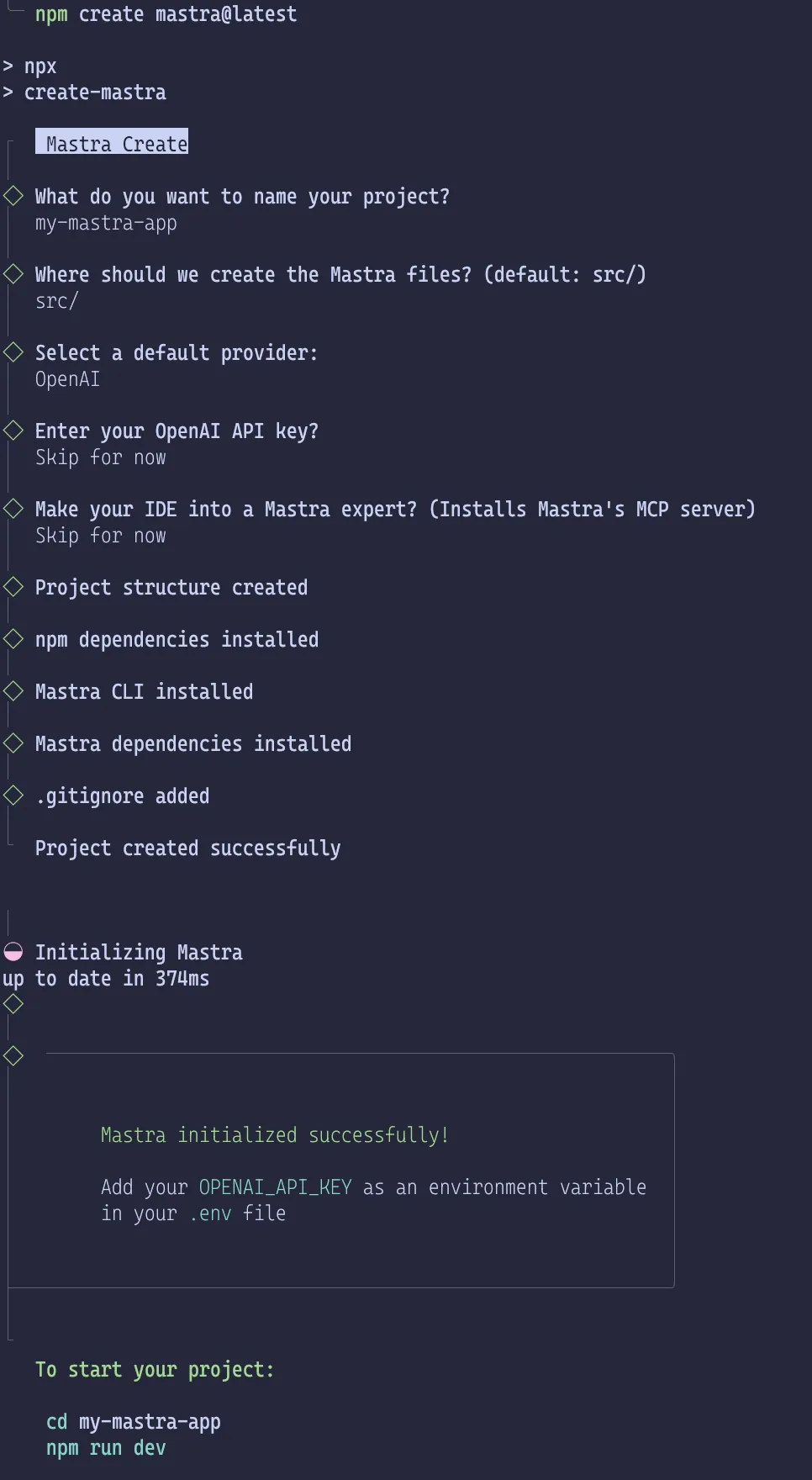
Create a mastra project per the docs.
1$ npm create mastra@latest
The mastra version is important. It's under active development; breaking changes and bugs are common. It is normal for a version upgrade to crash even if the previous version worked.
The command will ask some questions and generate a directory.
Directory structure
Initial structure:
1.2├── .env.example3├── .gitignore4├── package-lock.json5├── package.json6├── src7│ └── mastra8│ ├── agents9│ │ └── weather-agent.ts10│ ├── index.ts11│ ├── tools12│ │ └── weather-tool.ts13│ └── workflows14│ └── weather-workflow.ts15└── tsconfig.json16176 directories, 10 files
The official docs explain each file.
From the names, the initial project defines an agent that fetches weather info and answers or suggests activities. The workflow takes a city name, fetches weather, and proposes activities.
I'll explain agents and workflows in the next article. Here, the goal is just to run the sample with a local LLM.
Changes to use LM Studio
After generating the sample, you must configure the provider for your LLM. Here, we configure LM Studio's OpenAI-compatible API server.
The relevant doc is Model Providers | Getting Started | Mastra docs.
Now let's install packages and edit code.
package.json
First, install @ai-sdk/openai-compatible to use the LM Studio API:
1$ npm install @ai-sdk/openai-compatible
If other packages are outdated, run npx npm-check-updates -u to update them.
In my environment, package.json changed like this (I also changed license to MIT, but it's optional).
1diff --git a/package.json b/package.json2index f678078..44e95e6 1006443--- a/package.json4+++ b/package.json5@@ -11,22 +11,24 @@6},7"keywords": [],8"author": "",9- "license": "ISC",10+ "license": "MIT",11"type": "module",12"engines": {13"node": ">=20.9.0"14},15"dependencies": {16- "@ai-sdk/openai": "^2.0.50",17- "@mastra/core": "^0.20.2",18- "@mastra/libsql": "^0.15.1",19- "@mastra/loggers": "^0.10.15",20- "@mastra/memory": "^0.15.6",21- "zod": "^3.25.76"22+ "@ai-sdk/openai": "^2.0.52",23+ "@ai-sdk/openai-compatible": "^1.0.22",24+ "@mastra/core": "^0.21.1",25+ "@mastra/libsql": "^0.15.2",26+ "@mastra/loggers": "^0.10.16",27+ "@mastra/memory": "^0.15.7",28+ "zod": "^4.1.12"29},30"devDependencies": {31- "@types/node": "^24.7.2",32- "mastra": "^0.15.1",33+ "@types/node": "^24.8.1",34+ "mastra": "^0.17.0",35"typescript": "^5.9.3"36}37}
This diff is just an example; versions will differ if newer releases exist.
src/mastra/agents/weather-agent.ts
Next, add settings for LM Studio in src/mastra/agents/weather-agent.ts.
Import createOpenAICompatible from @ai-sdk/openai-compatible, call it with name, baseURL, and apiKey,
and bind the result to lmstudio.
name and apiKey can be anything.
Then, in weatherAgent, use lmstudio instead of openai and pass openai/gpt-oss-20b as the model.
1diff --git a/src/mastra/agents/weather-agent.ts b/src/mastra/agents/weather-agent.ts2index 7299c42..eaedfcb 1006443--- a/src/mastra/agents/weather-agent.ts4+++ b/src/mastra/agents/weather-agent.ts5@@ -1,8 +1,14 @@6-import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';7import { Agent } from '@mastra/core/agent';8import { Memory } from '@mastra/memory';9import { LibSQLStore } from '@mastra/libsql';10import { weatherTool } from '../tools/weather-tool';11+import { createOpenAICompatible } from "@ai-sdk/openai-compatible";12+13+const lmstudio = createOpenAICompatible({14+ name: "lmstudio",15+ baseURL: "http://localhost:1234/v1",16+ apiKey: "lm-studio",17+});1819export const weatherAgent = new Agent({20name: 'Weather Agent',21@@ -20,7 +26,7 @@ export const weatherAgent = new Agent({2223Use the weatherTool to fetch current weather data.24`,25- model: openai('gpt-4o-mini'),26+ model: lmstudio("openai/gpt-oss-20b"),27tools: { weatherTool },28memory: new Memory({29storage: new LibSQLStore({
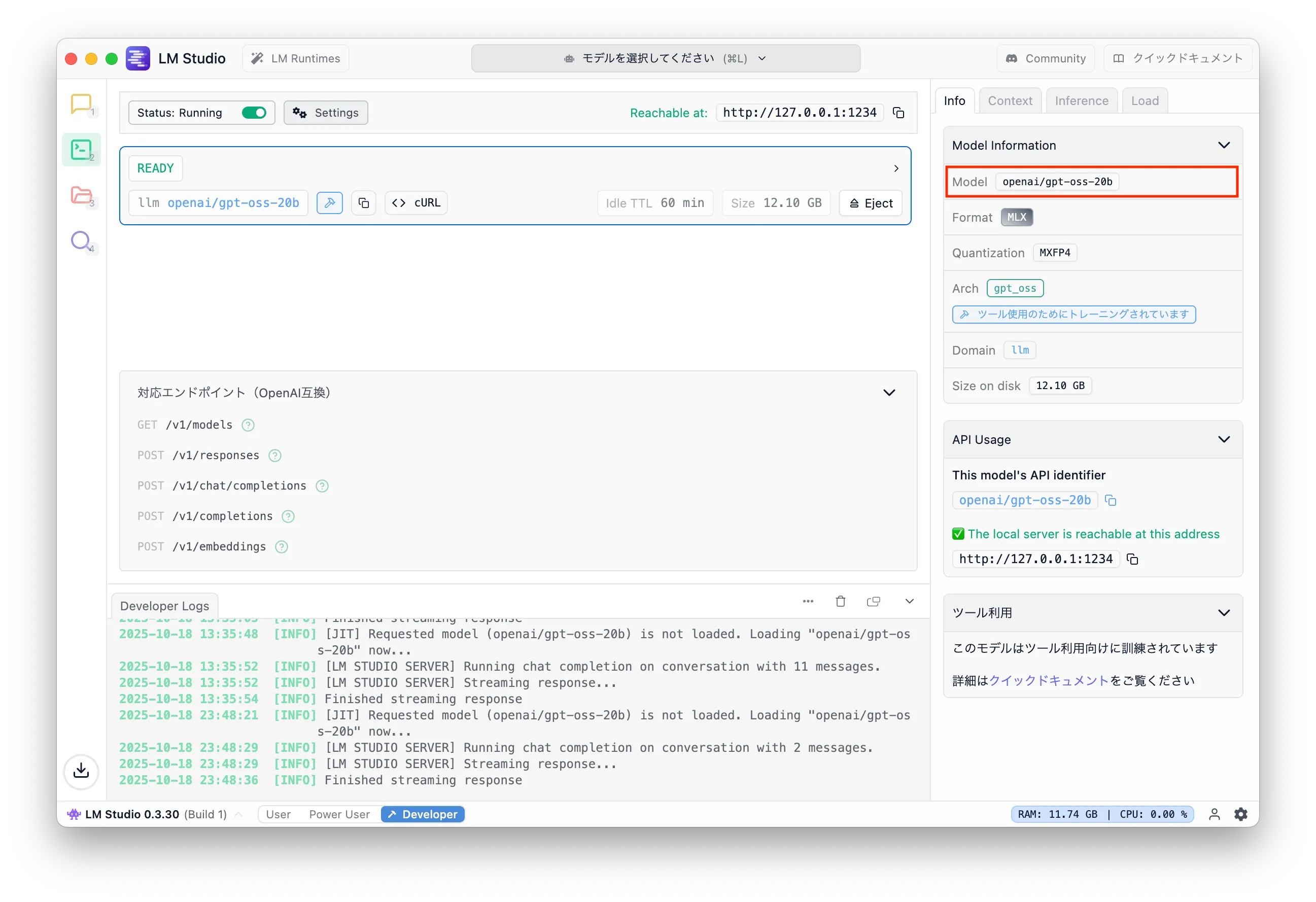
openai/gpt-oss-20b can be found in the LM Studio GUI.
.env
Finally, LM Studio requires LMSTUDIO_API_KEY to be set.
Create a .env file at the project root and set it.
1LMSTUDIO_API_KEY=lm-studio
Finally
Everything is ready. Just run it.
Running npm run dev outputs the following and starts the app on localhost:4111.
1$ npm run dev23> how-to-use-mastra@1.0.0 dev4> mastra dev56◐ Preparing development environment...7✓ Initial bundle complete8◇ Starting Mastra dev server...910mastra 0.17.0 ready in 721 ms1112│ Playground: http://localhost:4111/13│ API: http://localhost:4111/api1415◯ watching for file changes...
Open the browser and you should see this.
Since we just want to verify it works, click Weather Agent, open the chat UI, and send a prompt.
You will get a response (in English), as shown.
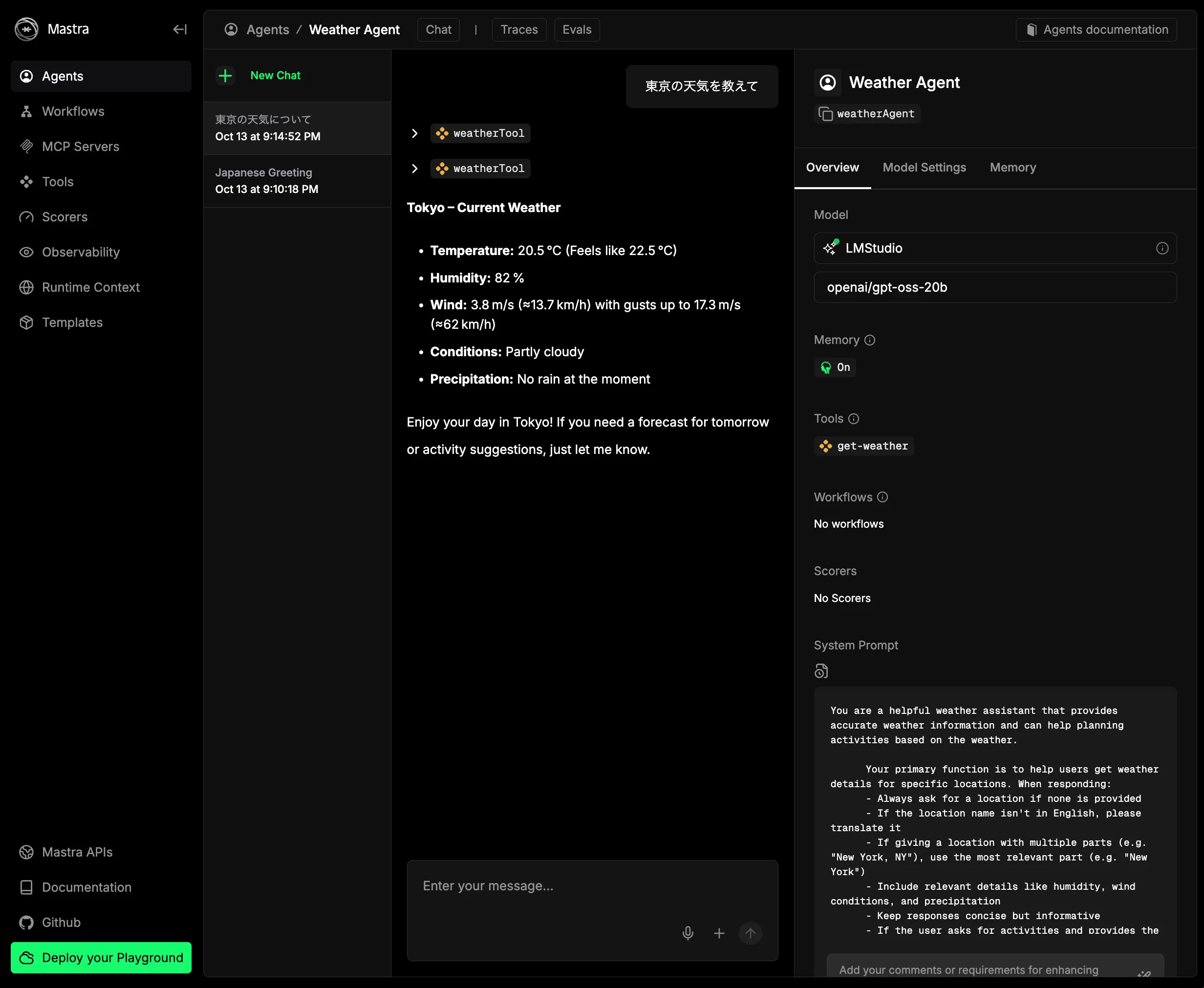
Now you have a working TypeScript environment for AI agents.
Summary
This article explained how to install Ollama and LM Studio, start an API server in LM Studio, and run the mastra sample. In the next article I will explain Ollama setup and the sample code details.
I want to see how far local LLM-based AI agents can go.
For AI agent development, I plan to follow Practical Introduction to AI Agents for Real-World Use (KS Information Science).
Footnotes
-
For NVIDIA/OpenAI the pickaxe is GPUs; for companies building AI services, the pickaxe is LLMs. ↩
-
Introducing Claude Haiku 4.5 \ Anthropic says Haiku 4.5 is 2x faster at 1/3 cost compared to a previous non-low-cost model (Claude Sonnet 4.0). ↩

